IMPORTANT PATIENT UPDATES
Haga clic aquí para información en español. Si está enfermo o tiene fiebre, tos, dificultad para respirar, o ha estado en contacto con alguien que tenga estos síntomas, por favor llame al (214) 540- 0704 para reagendar su cita.
General Information
If you are experiencing fever, cough, runny nose, shortness of breath or have been in contact with someone with these symptoms – DO NOT ENTER OUR LOBBY/OFFICE. Please call our scheduling department at 214-540-0704 or contact us via patient portal to get re-scheduled.
The safety of our patients and staff is very important to us. Therefore, masks are still required for all patients, visitors and staff at Rheumatology Associates. In addition, we are only allowing if necessary 1 essential visitor to accompany patients for communication or mobility assistance. Thank you for helping us keep our patients and staff safe and healthy.
What is the Delta Variant?
It is the predominant strain of the virus spreading in the United States at this time. It is twice as contagious as previous strains of the virus. The delta variant causes more severe illness than previous strains in unvaccinated patients.
What is the Omicron Variant?
It is a new variant first identified in November 2021 in Africa. The CDC expects the Omicron variant to spread more easily than the original SARS-CoV-2 virus. More information is still needed to know if this variant will cause more severe disease.
Are the vaccines effective against the Delta and Omicron Variants?
The vaccines are highly effective at preventing severe disease and death, including against the Delta variant. Current vaccines are also expected to protect against severe illness, hospitalizations, and deaths from the Omicron variant. However, breakthrough infections in people who are fully vaccinated are likely to occur.
Strategies to decrease the risk of contracting COVID-19 including the Delta and Omicron Variants
Patients receiving immune suppressing medications are at higher risk for severe COVID-19. One of the most important things that you can do is to get vaccinated if you have not already done it! If you are vaccinated, get the 3rd dose/booster.
Additionally, continue to wear masks, practice social distancing (stay 6 feet apart from others that you do not live with), and avoid crowds and poorly ventilated indoor places. Close contacts of immunocompromised people should get vaccinated if they haven’t already.
COVID-19 Vaccine Information (updated 12/28/2021)
As of December 11, 2021, there are three available vaccines against the coronavirus that causes Covid-19 in the US. These were developed by Pfizer, Moderna and Janssen (Johnson and Johnson). The benefit of vaccination is expected to far outweigh any risk from the vaccine. At Rheumatology Associates, we believe that getting vaccinated is very important, and we are urging our patients to choose either the Pfizer or the Moderna vaccines as recommended in recent guidelines by the American College of Rheumatology.
Should I get a 3rd COVID-19 vaccine if I am immunosuppressed?
In general, the answer is yes, a 3rd dose of the COVID-19 vaccine dose has been recommended for immunosuppressed patients 28 days after the second dose of either Pfizer or Moderna vaccine. Additionally, a booster dose of the Janssen vaccine should be administered 2 months after the first dose.
The CDC also recommends for those immunocompromised persons ≥18 years of age getting a booster of the Pfizer, Moderna, or Janssen vaccine at least 6 months after completing their third mRNA vaccine dose.
Should I get a booster COVID-19 vaccine if I am not immunosuppressed?
Yes. The CDC recommends all people aged 16 and above to receive a booster of the COVID-19 vaccine.
If you have questions about whether you should get a third dose or a booster of the COVID-19 vaccine, contact your provider.
What vaccine should I get for the 3rd dose or booster COVID-19 vaccine?
In general, the additional dose (3rd dose) should be the same mRNA vaccine as the primary series (if at all possible). So, if you got Moderna before, stick to Moderna; if you got Pfizer, stick to Pfizer. Heterologous (mix and match) booster doses can be used in people aged ≥18 years.
Why should I get a 3rd COVID-19 vaccine if I am immunosuppressed?
Similar to organ transplant recipients, patients with autoimmune diseases take immunosuppressants. Multiple studies have shown that these patients are less protected against COVID-19 than the general public in response to receiving the primary series of the COVID-19 vaccine. The vaccine itself is not harmful to these patients but their immunosuppressive medications limit their ability to develop antibodies against future infections if exposed. Two recent studies have shown that a third dose increases the response to the vaccine.
Should I get COVID-19 antibody testing to confirm immunity?
We do not support universal testing for COVID-19 antibodies to assess vaccine response at this time. Currently, there is no defined “optimal level” for COVID-19 antibodies, and no guidance on how to modify the vaccine strategy based on antibody levels. If you are on immune suppressing medications, we recommend you obtain a thirddose as described above.
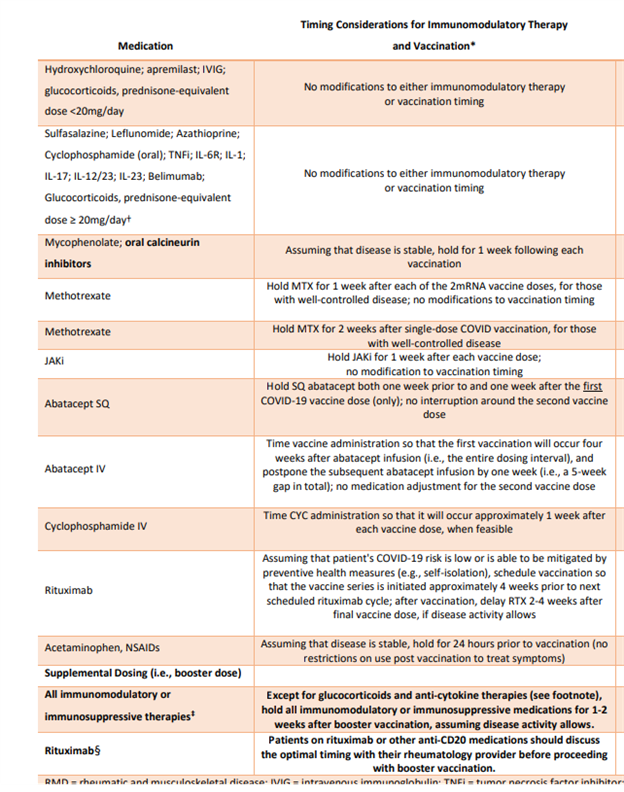
Should I adjust my medications around the time of vaccination?
When getting ready to receive your vaccine, please be aware that The American College of Rheumatology has published guidance regarding the use of immune suppressing medications around the time of the vaccine.
Based on the available information, patients taking the following medications may continue them without changeduring their primary vaccine series or third dose/booster: Prednisone <20 mg/day (or glucocorticoid equivalent), Actemra, Kevzara, Cosentyx, Taltz, Tremfya, Stelara, Kineret, Ilaris.
Patients receiving Sulfasalazine, Leflunomide (Arava), Azathioprine (Imuran), Methotrexate, mycophenolate (CellCept, Myfortic), Xeljanz, Olumiant, Rinvoq, Orencia (both self-injections and intravenous), Rituximab (truxima, ruxience, riabni), Tacrolimus, Cyclosporine, Benlysta, oral Cyclophosphamide, and intravenous Cyclophosphamide may benefit from temporarily holding the medication when receiving the vaccine if their disease is well controlled.
Patients taking Enbrel (erelzi, eticovo), Humira (amjevita, cyltezo, hyrimoz, hadlima, hulio), Simponi, Simponi Aria, Remicade (Inflectra, Renflexis, Ixifi, Avsola), or Cimzia should consult with their provider regarding whether to continue or hold the medication during vaccination.
Before holding or making any changes to your medications, please contact your provider.
Additional recommendations include holding Acetaminophen and NSAID’s (over the counter or prescription) for 24 hours prior to vaccination. There are no recommended restrictions on use post vaccination to treat symptoms.
Where can I get a vaccine for Covid-19?
Rheumatology Associates is not offering vaccination services against COVID-19 at this time, but please check our website frequently for new updates. If you are trying to find where to get vaccinated please check COVID-19 Vaccine Information (texas.gov) or call 211 for a referral to a local vaccine provider.
What should I do if I am exposed to COVID-19?
If you have a high-risk exposure, such as a close household contact, please contact your rheumatologist for instructions on whether to hold your immune suppressing medication, and whether you may be a candidate for a one-time treatment which may reduce your risk of contracting COVID-19.
Monoclonal antibody treatment: People who are not fully vaccinated, or who are on immune suppressing medication and therefore may not mount a full response to the vaccine, may be a candidate for a monoclonal antibody treatment which may reduce the risk of developing COVID-19 infection. This treatment is a one-time dose, given either intravenously or subcutaneously, and must be given within the first three days after exposure.
For more information about where to get monoclonal antibody treatment, visit https://provider.covid-frontline.com/antibody-resource-guide/
What should I do if I am diagnosed with Covid-19?
If you have confirmed or strongly suspected COVID-19, please contact your PCP for instruction about where to go to be evaluated or get tested or go to urgent care or ER if your symptoms indicate you require immediate medical attention. Let your rheumatologist know about your diagnosis as he/she may have specific recommendations on what to do.
In general, if you are on immune suppressing medication (such as sulfasalazine, methotrexate, azathioprine, CellCept, Cytoxan, any injectable or infusion medication for autoimmune disease (Xeljanz, Olumiant, or Rinvoq), we recommend stopping the medication immediately. This will help your body be better able to fight off any infection. Once you are clearly improving and the infection is resolving, you can resume your immune suppressing medication.
If you are on Plaquenil (hydroxychloroquine), you may continue it.
Monoclonal antibody treatment: People with a confirmed + COVID-19 infection who are at increased risk for severe COVID-19 may benefit from a one-time intravenous treatment which can reduce the risk of developing severe COVID-19. This treatment may only be given to outpatients and must be given in the first ten days of symptoms. Many local hospital emergency rooms are administering these treatments. Please contact your rheumatologist, PCP, and/or the local ER to ask if you are a candidate and how to obtain the treatment.
What is pre-exposure prophylaxis and who may be a candidate?
Pre-exposure prophylaxis refers to the administration of a preventative treatment for COVID-19 in patients who are not infected. This is reserved for certain immune compromised individuals who may not mount an adequate immune response to COVID-19 vaccination, or those who have a history of severe adverse reactions to a COVID-19 vaccine and therefore cannot receive one and need an alternative prevention option.
The FDA has recently approved for emergency used a different type of monoclonal antibody called Evusheld for pre-exposure prophylaxis. This medication is still not available and we do not have details yet about when and where it may be available in Texas. We also do not know which types of patients will be prioritized to receive this drug initially, and supplies are likely to be limited. We will update the website with information when we have more details to share.
Be aware that vaccines are still the best available defense against COVID-19.
We recommend using the CDC’s Coronavirus Self-Checker, it is an interactive clinical assessment tool that will assist individuals ages 13 and older, on deciding when to seek testing or medical care if they suspect they or someone they know has contracted COVID-19 or has come into close contact with someone who has COVID-19.
.

RESOURCES
© RHEUMATOLOGY ASSOCIATES, 2024.
